Leave Your Message
In the world of thermal management, Plate Heat Transfer technologies are essential for efficiency. As industries demand higher performance, understanding these methods becomes crucial. This article explores the top Plate Heat Transfer technologies to watch for in 2026.
With an emphasis on energy efficiency, these technologies represent evolving solutions. Plate Heat Transfer systems offer compact designs and impressive heat exchange rates. They play a vital role in heating, cooling, and industrial applications. However, not all systems are perfect; some may face challenges with maintenance and cost.
Designing an effective Plate Heat Transfer system requires careful consideration. Effective use of materials and energy recycling should not be overlooked. Industry players must adapt to new technologies while reflecting on past practices. The future of Plate Heat Transfer holds promise, but awareness of limitations is essential.


In 2026, plate heat transfer technologies are evolving rapidly. These innovations focus on efficiency and sustainability. Enhanced designs are improving heat transfer rates significantly. The use of advanced materials is becoming more common. This shift allows for better thermal conductivity and durability.
Many industries now prioritize energy conservation. Plate heat exchangers, for instance, demonstrate excellent performance in various applications. However, some designs can be complex and challenging to maintain. Engineers face hurdles in optimizing these systems for specific needs. Solutions often require trial and error, which delays project timelines.
The future of plate heat transfer technologies holds promise. Researchers are exploring nanostructured surfaces for improved performance. Yet, scalability remains a concern. Innovations must translate effectively from labs to real-world applications. Balancing cost-effectiveness and efficiency is a persistent challenge. As the industry evolves, reflection on past designs will be crucial for future success.
Emerging trends in plate heat exchanger design focus on maximizing efficiency and sustainability. Innovative designs can reduce maintenance costs and energy consumption. New materials and manufacturing techniques allow for lighter and more compact units. Enhanced surface geometries improve heat transfer performance. These advancements lead to better thermal efficiency in various applications.
Sustainability is a critical consideration. Many technologies are now being developed with environmental impacts in mind. Reduced carbon footprints and better recyclability rates are priorities. However, not all innovations are perfect. Some designs face challenges in integrating with existing systems. Compatibility issues can arise, causing delays in implementation.
Moreover, there is ongoing research into nanotechnology and microchannel designs. These approaches show great promise but require extensive testing. The balance between cost, performance, and environmental impact is delicate. Challenges remain in scaling up these developments for widespread use. Continuous optimization is necessary to make these technologies practical and accessible to all.
This chart illustrates the efficiency percentages of emerging plate heat transfer technologies anticipated for 2026. Each technology represents notable advancements in design and performance within the industry.
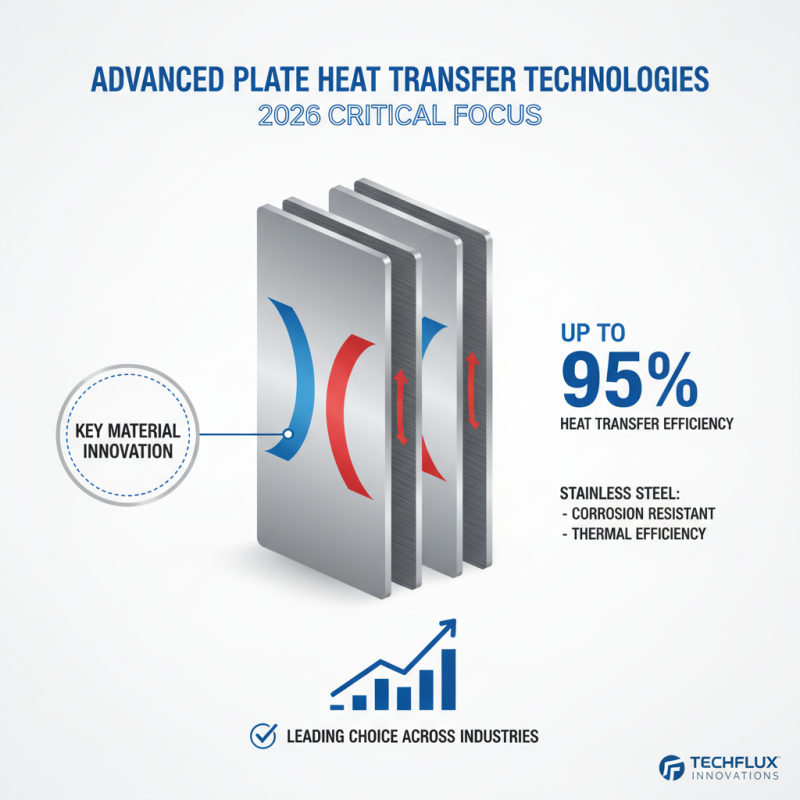
In 2026, the focus on advanced plate heat transfer technologies is critical. Key materials drive innovations in this field. Stainless steel remains a staple, known for its corrosion resistance and thermal efficiency. Research highlights that stainless steel plate heat exchangers can achieve up to 95% heat transfer efficiency. This remarkable statistic makes it a leading choice across industries.
Copper is another vital material. Its exceptional thermal conductivity enhances heat transfer performance significantly. Studies indicate that copper plates can increase the energy efficiency of heat exchangers by approximately 30%. However, costs remain a barrier, as copper tends to be pricier than alternatives. Some manufacturers struggle with balancing cost and performance.
Polymers, including PEEK and PTFE, are gaining traction. These materials provide resistance to aggressive chemicals, which is useful in specific applications like food processing. Yet, their adoption is limited due to temperature constraints. These examples highlight the diversity in materials used for plate heat transfer solutions. Each material offers advantages, but challenges exist in efficiency, cost, and application suitability.
The advancements in plate heat exchanger manufacturing processes are remarkable. Various materials are being utilized to enhance efficiency and durability. For instance, some manufacturers are experimenting with innovative alloys. These materials can withstand higher pressures and temperatures. This makes them more reliable in challenging environments.
Moreover, automation is becoming integral in manufacturing. This shift reduces human error and boosts precision. However, not all manufacturing facilities have transitioned smoothly. Some still rely on outdated methods. This inconsistency can affect product quality. Striking a balance between innovation and tradition remains a challenge for many.
Investing in research and development is crucial. New techniques, like 3D printing, are emerging. This allows for complex designs that traditional methods cannot achieve. Yet, there are learning curves and costs involved. Many companies are still figuring out how to integrate these technologies effectively. It’s a journey with ups and downs, requiring constant adaptation and reflection.
Plate heat transfer technologies are pivotal in various industries. They excel in sectors like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing. Their efficiency allows for compact designs, which is essential in space-constrained environments. These technologies optimize thermal exchange, enhancing performance and reducing energy costs.
In food processing, plate heat exchangers ensure safe pasteurization. They maintain quality while preserving flavors and nutrients. The pharmaceutical industry benefits from precise temperature control during production. However, there are challenges. Fouling can affect efficiency, requiring regular cleaning and maintenance. Operators must balance performance with upkeep costs.
The chemical industry demands reliable systems for handling corrosive substances. Custom designs can accommodate specific needs, but they often come with higher investments. Operators must weigh these costs and understand their long-term benefits. Embracing plate heat transfer technologies means constantly adapting to industry demands and potential drawbacks.
| Technology | Applications | Industry Demands | Efficiency Rating | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hybrid Plate Heat Exchangers | Oil and gas, chemical processing | High efficiency, space-saving | 95% | Increased use of AI for monitoring |
| Corrugated Plate Heat Exchangers | Food processing, HVAC systems | Demand for energy-efficient solutions | 90% | Growing preference for compact designs |
| Welded Plate Heat Exchangers | Pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals | High-pressure applications | 92% | Advancements in material technology |
| Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers | Water cooling, district heating | Versatility and ease of maintenance | 88% | Integration with renewable energy systems |
| Brazed Plate Heat Exchangers | Refrigeration, marine services | Compact design, lightweight solutions | 94% | Focus on sustainability and lower emissions |






