Leave Your Message
In the realm of industrial heat transfer solutions, the Plate Exchanger stands out as a vital component across various applications. According to a recent market analysis by Mordor Intelligence, the global heat exchanger market is expected to reach USD 21.56 billion by 2025, with plate exchangers increasing their share due to their compact design and efficiency. These devices utilize a series of thin plates to transfer heat between two fluids, achieving greater thermal efficiencies and space savings compared to traditional shell-and-tube heat exchangers.
Furthermore, the demand for energy-efficient technologies in sectors such as chemical processing, oil and gas, and HVAC is propelling the growth of the Plate Exchanger segment. Research from Research and Markets highlights that the push towards sustainability and cost reductions is driving industries to adopt more effective heat exchange solutions. As energy consumption regulations become stricter, businesses are turning to plate exchangers to enhance operational efficiency while reducing their carbon footprint. This article explores the functionality, advantages, and various industrial applications of Plate Exchangers, shedding light on why they are poised to remain a cornerstone in heat transfer technology through 2025 and beyond.
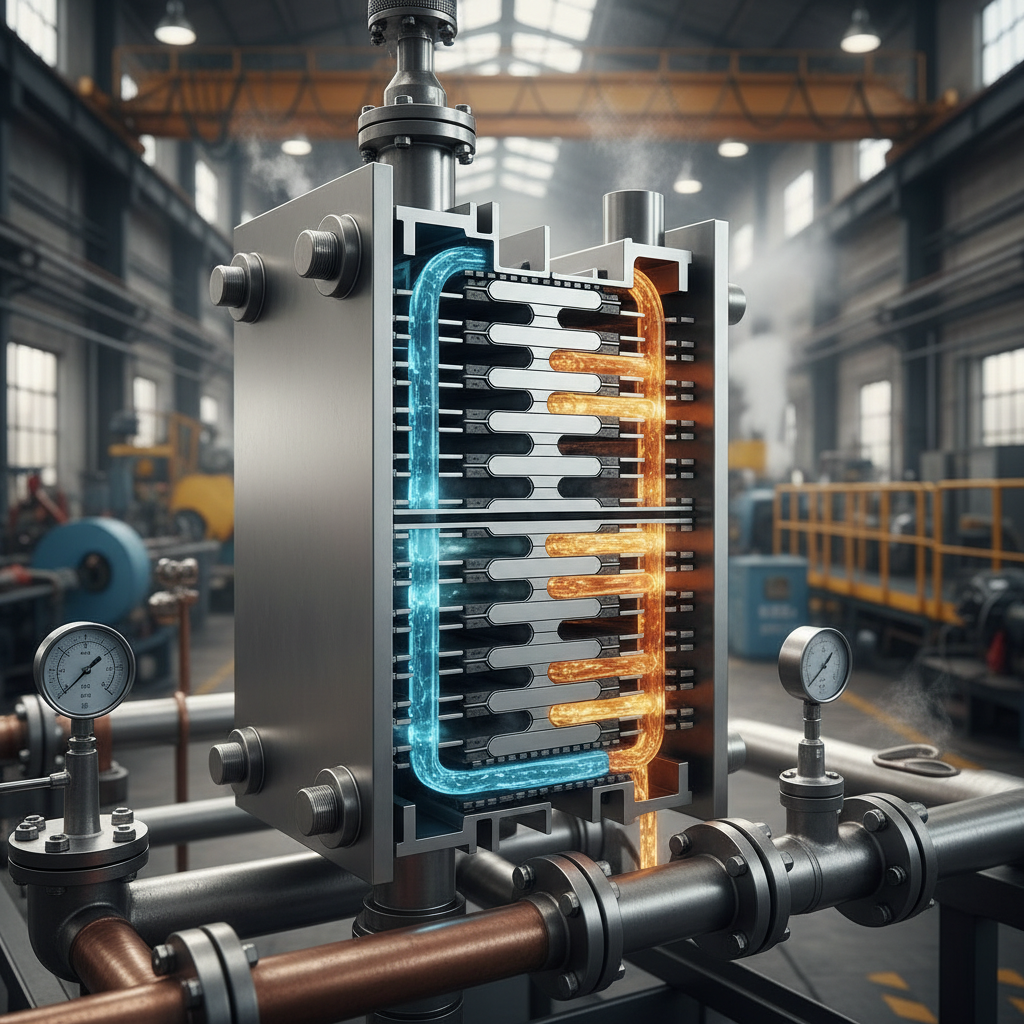

Plate exchangers, often referred to as plate heat exchangers (PHE), are essential components in many industrial applications for heat transfer processes. These devices consist of multiple thin plates arranged in a frame, creating a series of channels for the fluids to flow through. When hot and cold fluids pass through these channels, heat is transferred from the hot to the cold fluid without the two ever mixing. This efficient design allows PHEs to transfer large amounts of heat in a compact space, making them ideal for industries such as food processing, chemical production, and HVAC systems.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global plate heat exchanger market is expected to grow from $3.9 billion in 2020 to $5.2 billion by 2025, reflecting an annual growth rate of around 6.3%. This surge is attributed to the increasing demand for energy efficiency and sustainable practices in industrial operations. Additionally, plate exchangers contribute significantly to reduced operational costs and environmental footprints, as they require less energy and less space compared to traditional shell-and-tube heat exchangers. The ability to handle a variety of fluids, including viscous liquids and steam, further underscores the versatility and critical role of plate heat exchangers in enhancing productivity across various sectors.
Plate heat exchangers (PHEs) are essential components in various industrial applications, designed to efficiently transfer heat between two fluids while maintaining their separation. The key components of a plate heat exchanger include plates, gaskets, frame, and inlet/outlet connections. The plates, typically made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials, are carefully engineered for optimal surface area and flow design, which enhances the heat transfer efficiency by promoting turbulence—resulting in better thermal performance compared to traditional exchangers.
In terms of operational efficiency, a well-designed plate heat exchanger can offer heat transfer coefficients ranging from 2000 to 5000 W/m²K, which is significantly higher than shell-and-tube heat exchangers. The gaskets play a crucial role in sealing the spaces between the plates, preventing mixing of the fluids and ensuring that heat transfer occurs effectively. The frame provides structural integrity, holding the plates in place and allowing for easy maintenance and cleaning. According to Industry Research, the global market for plate heat exchangers is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 7% between 2021 and 2026, driven by advancements in energy efficiency and increasing demand in sectors such as HVAC, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer Plates | Thin plates made of metal that provide a large surface area for heat exchange. | Facilitate heat transfer between two fluids, enhancing efficiency. |
| Frame | The structural component holding the plates together under pressure. | Maintains the alignment and spacing of plates while allowing fluid flow. |
| Gaskets | Seals around the edges of the plates to prevent leaks. | Ensure that the fluids do not mix and are directed through the plates. |
| End Plates | Plates at the ends of the heat exchanger providing support and sealing. | House the inlet and outlet ports for the fluids. |
| Support Plates | Specially designed plates that add strength to the assembly. | Support the weight of the plates and maintain structural integrity. |
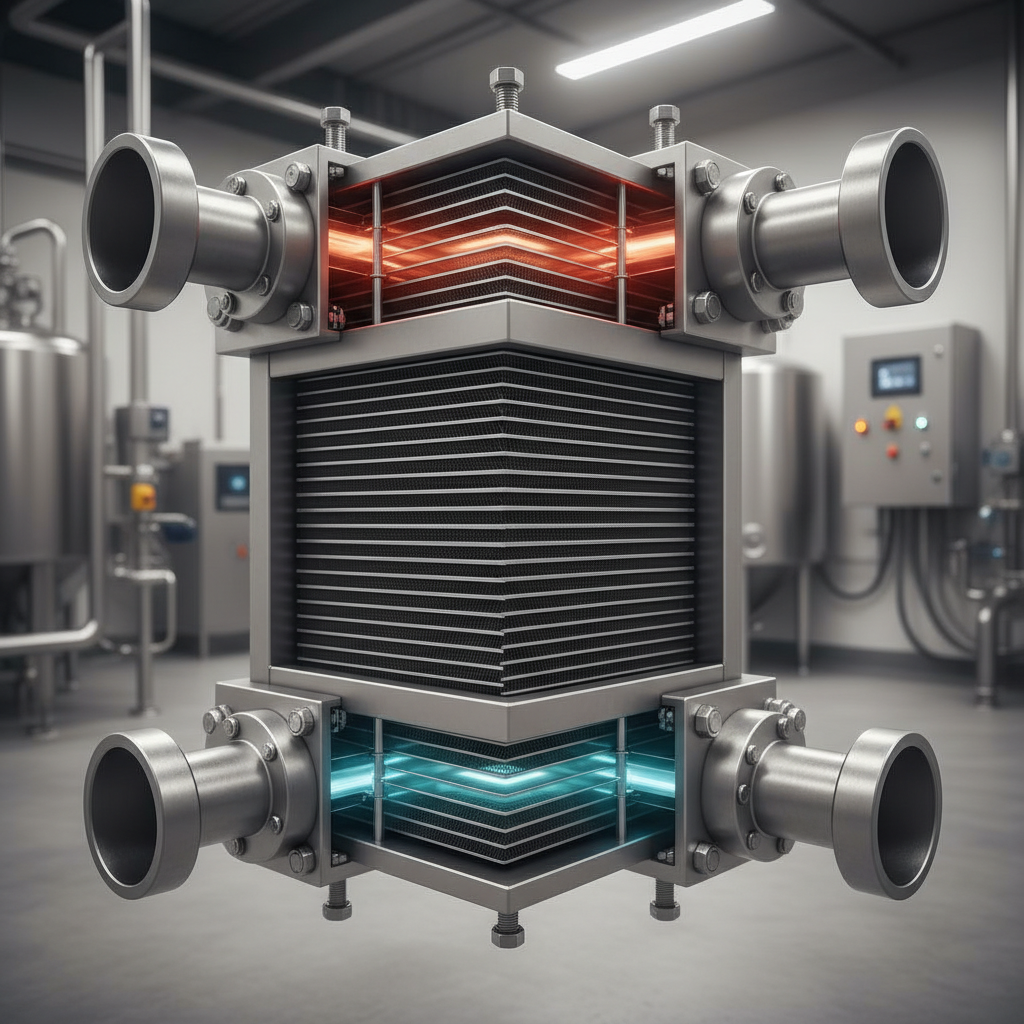 Plate exchangers are crucial components in various industrial applications, primarily used for effective heat transfer between two fluids. They consist of many thin plates stacked together, creating channels for the fluids to flow. This design allows for a large surface area in a compact unit, facilitating efficient heat exchange. The counterflow arrangement of fluids in plate exchangers further optimizes thermal performance, enabling industries to achieve desired temperature regulation while minimizing energy losses.
Plate exchangers are crucial components in various industrial applications, primarily used for effective heat transfer between two fluids. They consist of many thin plates stacked together, creating channels for the fluids to flow. This design allows for a large surface area in a compact unit, facilitating efficient heat exchange. The counterflow arrangement of fluids in plate exchangers further optimizes thermal performance, enabling industries to achieve desired temperature regulation while minimizing energy losses.
In terms of energy efficiency, plate exchangers significantly enhance performance by reducing the amount of energy required for heating or cooling processes. By maximizing heat recovery, these systems can lower the overall energy consumption within industrial operations. This not only leads to cost savings but also contributes to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with sustainable practices. Industries such as food processing, chemical manufacturing, and HVAC systems are increasingly adopting plate exchangers due to their ability to provide reliable thermal management while enhancing overall energy efficiency.
Plate heat exchangers (PHEs) are widely utilized in various industrial applications due to their efficiency in transferring heat between two or more fluids. These systems are particularly effective in industries such as chemical processing, food and beverage production, and HVAC systems. Their design allows for large surface areas in a compact volume, facilitating effective heat transfer while minimizing space requirements. This makes them ideal for processes that need temperature regulation without significant energy loss.
One common industrial application of plate heat exchangers is in the food and beverage industry, where they are used for pasteurization and cooling processes. The ability to quickly adjust flow rates helps maintain product quality and safety standards. Similarly, in chemical processing, PHEs enable precise temperature control during reactions, improving efficiency and yielding better results.
**Tips**: When selecting a plate heat exchanger, consider the fluid properties and required temperature changes to ensure optimal performance. Regular maintenance and cleaning can also enhance the efficiency and lifespan of the unit. Moreover, integrating sensors to monitor flow rates and temperature can help in optimizing the heat exchange process, leading to substantial energy savings and operational benefits.
Plate exchangers are critical components in various industrial applications, particularly in processes requiring efficient heat transfer. To ensure these systems function optimally, maintenance and operational considerations are paramount. Regular inspection and cleaning of plate exchangers can significantly reduce the risk of fouling, a common issue that can lead to decreased efficiency and higher operational costs. According to a report by the Heat Exchange and Transfer Association, proactive maintenance can improve system efficiency by up to 30%, which is crucial in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and energy.
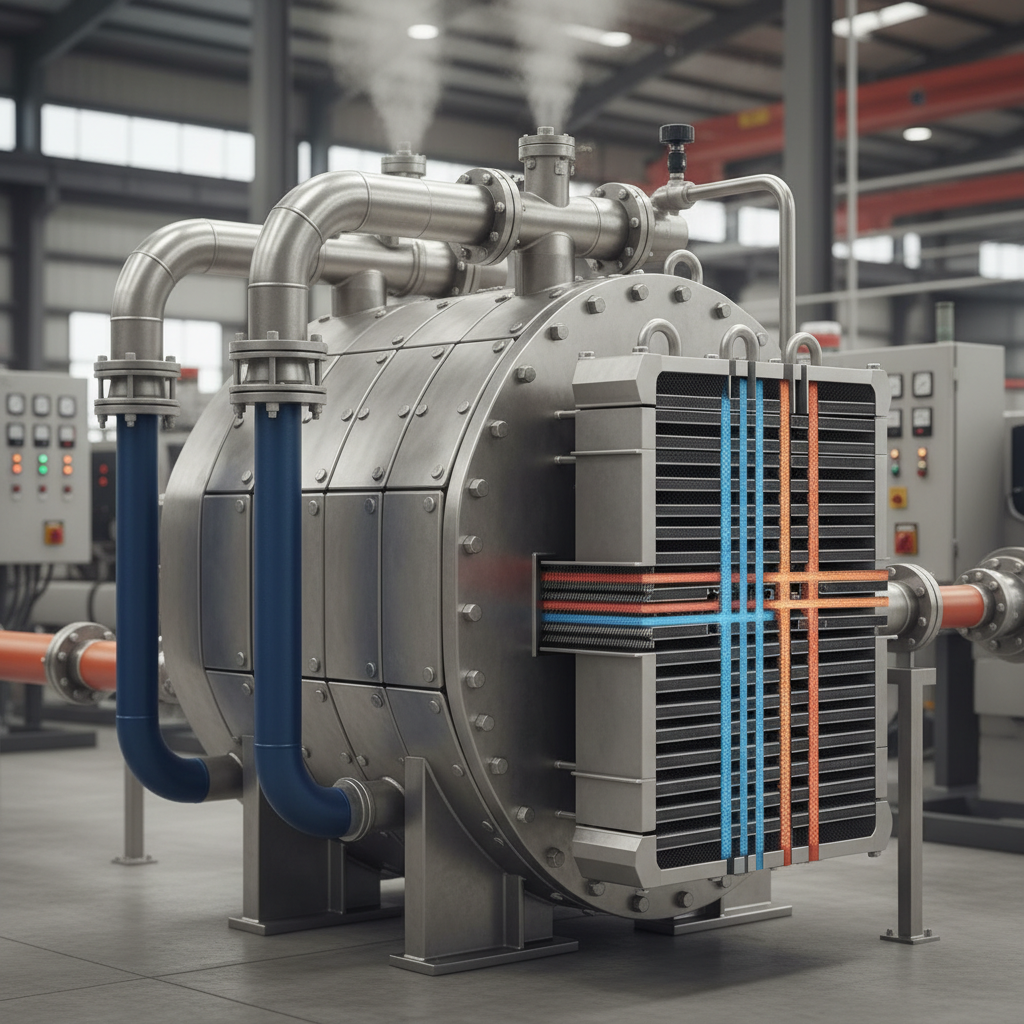

Operational considerations also play a vital role in the efficacy of plate exchangers. Monitoring flow rates and pressure drops is essential for early detection of any potential issues. A study from the International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer indicates that maintaining the operational parameters within manufacturer specifications can enhance the lifespan of the exchanger, with optimal performance observed when operating below 80% of design capacity. Additionally, implementing a routine maintenance schedule based on the manufacturer's guidelines can help prevent unexpected downtimes and ensure continuous operation, ultimately leading to significant cost savings and increased productivity in industrial applications.