Leave Your Message
Heat Exchanger PHE, or Plate Heat Exchanger, plays a critical role in various industries. This device transfers heat between two fluids, utilizing metal plates for efficient heat exchange. Its compact size makes it a preferred choice for many applications, from food processing to chemical production.
The design of Heat Exchanger PHE allows for a maximized surface area, enhancing thermal performance. Each plate creates a unique flow pattern, ensuring effective heat transfer. However, maintenance can be challenging. Over time, fouling may occur, impacting efficiency. Regular cleaning and inspections are necessary to maintain optimal performance.
Heat Exchanger PHE is not without its flaws. It may leak under pressure, leading to fluid contamination. Users must remain vigilant for signs of wear. Understanding these shortcomings can help prevent costly failures and ensure prolonged service life. Being aware of these aspects is crucial for those relying on this technology in their operations.

Plate Heat Exchangers (PHE) (PHE) play a vital role across various industries. These devices facilitate efficient heat transfer between two fluids without mixing them. They are especially crucial in processes requiring temperature control. According to recent industry reports, PHEs can achieve heat transfer efficiencies up to 90%. This efficiency significantly impacts energy consumption and operational costs.
In sectors such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and HVAC, PHEs are indispensable. They occupy less space than traditional shell-and-tube heat exchangers, which is a critical factor in urban installations. However, PHEs are not without challenges. Their plates can become fouled over time, which is a concern. Regular maintenance is essential, but it may lead to operational downtime. Interestingly, many facilities struggle with maintenance schedules, potentially decreasing efficiency.
Data indicates that investments in modern PHE technology could reduce energy use by 15% to 30%. Yet, the initial costs can deter some companies. Balancing upfront investments with potential savings is often complex. Despite these challenges, the importance of PHEs continues to grow. They shape future sustainable designs in industrial processes. The need for heat exchangers will only increase as industries focus on energy efficiency and environmental impacts.
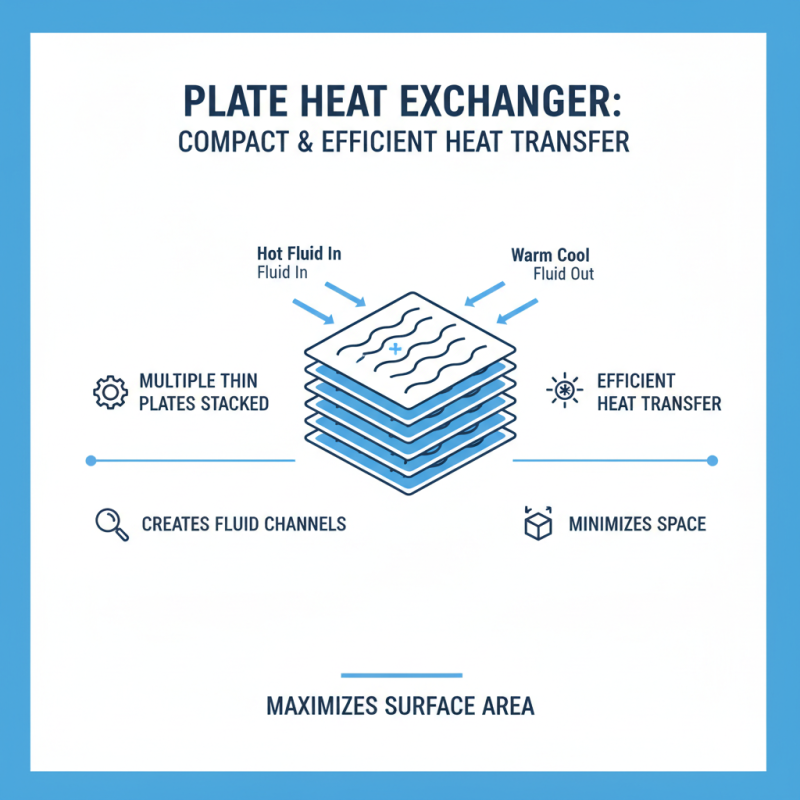
Plate heat exchangers (PHE) are crucial in transferring heat between two fluids. They consist of multiple thin plates stacked together. The design allows for efficient heat transfer while minimizing space. These plates create channels where the fluids flow. This setup maximizes surface area for heat exchange. The compact design is beneficial in various industries.
Key components of a PHE include the plates, gaskets, and frame. Plates are typically made from stainless steel. They have a corrugated design to enhance heat transfer. Gaskets seal the edges, preventing leaks. The frame holds the plates in place and allows for easy maintenance. Choosing the right materials is essential for durability.
Tips: Consider the flow arrangement carefully. Counterflow systems can be more efficient. Ensure regular cleaning to maintain performance. Dirty plates can hinder effective heat exchange. Monitor temperature differences to optimize operation. Regular assessments can reveal potential issues early, saving time and costs.
In a plate heat exchanger (PHE), heat transfer relies on the principles of conduction and convection. Fluids flow through alternating plates, enhancing thermal efficiency. According to the Heat Exchanger World Market report, the global PHE market is projected to grow 8.5% annually. This trend reflects the increasing energy demands across industries.
Heat transfer efficiency depends on design factors, such as flow arrangement and surface area. The overall thermal conductivity can increase if the temperature difference between the two fluids is substantial. A well-designed PHE can achieve a heat transfer coefficient of around 2,000 W/m²K. Poor design can lead to inefficiencies, indicating the necessity for careful calculations.
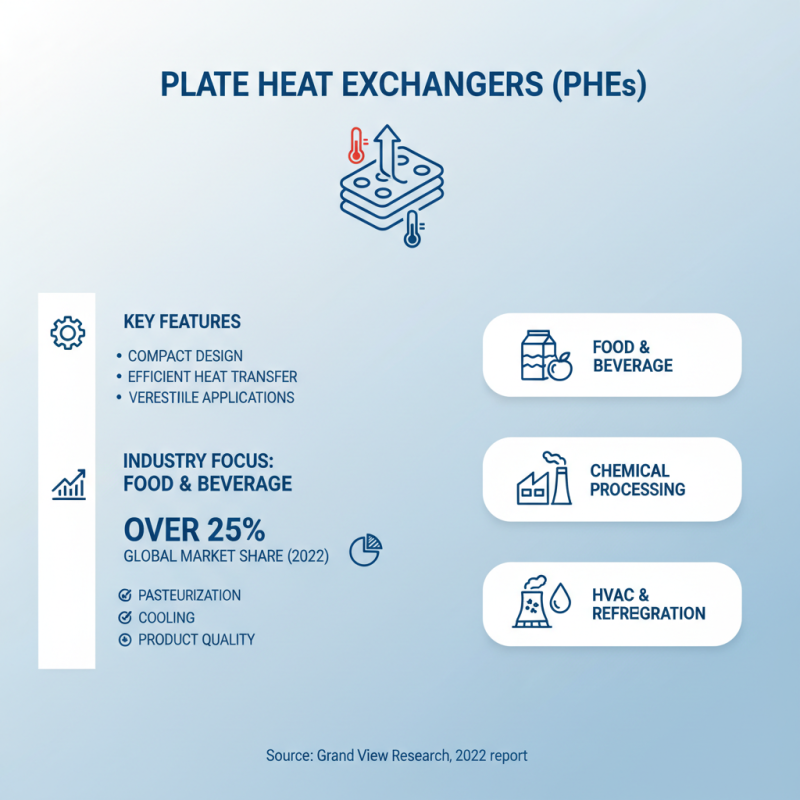
Plate heat exchangers (PHEs) are widely used across various industries. Their compact design allows efficient heat transfer, making them ideal for many applications. In the food and beverage sector, PHEs help maintain product quality during processes like pasteurization and cooling. According to a report by Grand View Research, the food and beverage segment accounted for over 25% of the global plate heat exchanger market in 2022.
In the chemical industry, PHEs assist in controlling the temperature of reactive processes. They improve energy efficiency drastically, which is vital for companies seeking sustainable practices. A study by the International Energy Agency shows that energy efficiency improvements in chemical processing can reduce emissions significantly. PHEs also play a crucial role in HVAC systems, where they enhance energy recovery and improve indoor environments.
While PHEs are efficient, there are challenges. Fouling, a common issue, can lead to decreased performance. Regular maintenance is needed to ensure optimal function. Many industries still face the dilemma of balancing efficiency and maintenance costs. Identifying the right design and materials is essential for overcoming these hurdles.
Plate heat exchangers (PHEs) are popular due to their efficiency and compact design. They utilize metal plates to transfer heat between two fluids. This design provides a large surface area in a small space. However, there are both advantages and limitations to consider in industrial processes.
One significant advantage of PHEs is their high thermal efficiency. Studies show PHEs can achieve heat transfer efficiency over 90%. This leads to lower energy consumption and reduced operating costs. Additionally, they are easy to clean and maintain. Regular maintenance can prolong their lifespan and help prevent fouling.
On the downside, PHEs may face issues related to pressure drops. A high flow rate can lead to significant pressure loss, impacting performance. Furthermore, the risk of fluid leakage exists, especially when handling corrosive fluids. This can lead to environmental concerns. Therefore, proper selection and material choices are crucial.
Tip: Regularly inspect and clean your PHE to ensure optimal performance. Also, consider fluid properties when selecting materials for construction. Pay attention to the environment and operations to avoid unnecessary risks.
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Type of Heat Exchanger | Plate Heat Exchanger (PHE) |
| Working Principle | Heat transfer occurs through metal plates with fluids moving in channels between them. |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | High efficiency due to large surface area available for heat transfer. |
| Advantages | Compact design, easy to clean, suitable for high heat transfer applications. |
| Limitations | Susceptible to fouling, pressure drop can be high, requires careful selection of materials. |
| Applications | Food processing, pharmaceuticals, HVAC systems, and chemical industries. |