Leave Your Message
Optimizing the performance of a heat exchanger, particularly a Plate Heat Exchanger (PHE), is crucial for enhancing energy efficiency and operational effectiveness in various industrial applications. As industries increasingly focus on sustainability and cost reduction, understanding the intricacies of Heat Exchanger PHE systems has become ever more significant. Effective heat exchanger operation not only contributes to reduced energy consumption but also prolongs equipment lifespan and minimizes maintenance needs. In this context, mastering the optimization techniques for PHEs is essential.
This article presents ten essential tips for maximizing the performance of Heat Exchanger PHE units. Each tip is grounded in best practices and proven strategies that can significantly impact the heat transfer efficiency, pressure drop, and overall system reliability. By implementing these recommendations, engineers and facility managers can navigate the complexities of PHE design and operation, leading to improved thermal performance, reduced operational costs, and enhanced system reliability. Embracing these strategies will not only foster better management of thermal processes but also support broader energy conservation goals within the industry.
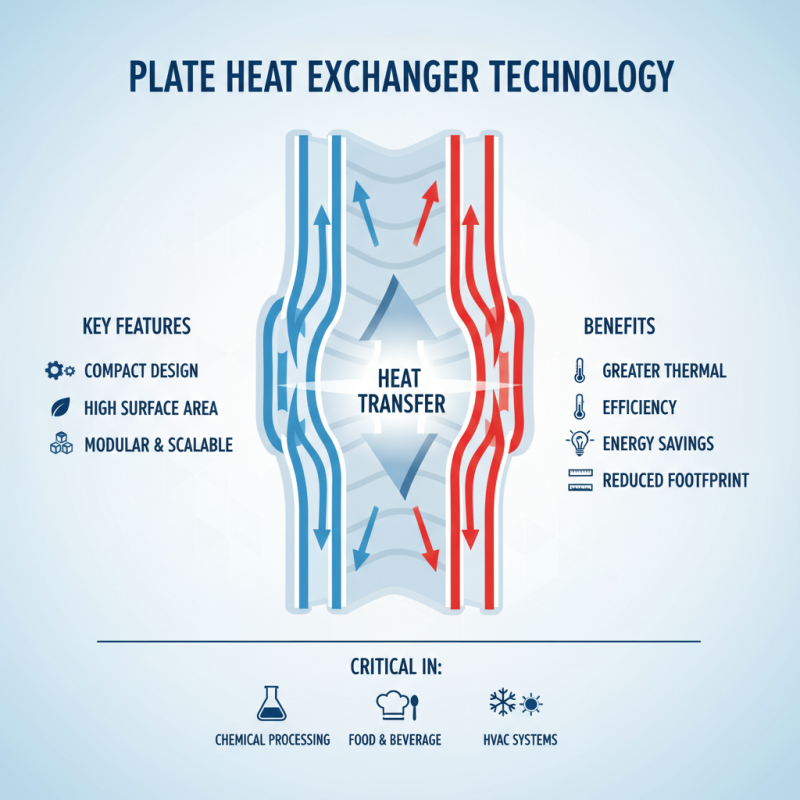
Plate Heat Exchangers (PHE) are a critical component in many industrial processes, serving to efficiently transfer heat between two fluids. Their design consists of multiple plates that create channels for fluid flow, allowing for maximum surface area contact while minimizing space requirements. This unique structure enables PHEs to achieve greater thermal efficiency compared to traditional heat exchangers, making them ideal for applications in the chemical, food, and HVAC industries.
Understanding the basics of PHEs is essential for optimizing their performance. The thermal performance is influenced by several factors, including the plate geometry, flow arrangement, and the properties of the fluids involved. Proper maintenance and regular inspections can further enhance their efficiency and longevity. Additionally, addressing common issues such as fouling and pressure drops is critical to maintain optimal operating conditions. By focusing on these fundamentals, operators can ensure that their plate heat exchangers deliver reliable and efficient performance throughout their service life.
In the realm of heat exchanger performance, key performance indicators (KPIs) are essential for assessing efficiency. One primary KPI is the heat transfer coefficient, which directly affects the overall heat transfer effectiveness. According to the Heat Exchanger Design Handbook, optimizing the heat transfer coefficient can lead to up to a 30% increase in performance when using plate heat exchangers (PHE). Factors influencing this coefficient include fluid properties, flow arrangement, and surface area, all of which require careful consideration during the design phase.
Another critical metric is the pressure drop across the heat exchanger. Excessive pressure drop can indicate inefficient operation and result in higher pumping costs, affecting the overall system energy efficiency. The average pressure drop for PHEs should ideally not exceed 5-10% of the inlet pressure; exceeding this range often signals the need for redesign or cleaning. Regular monitoring of these KPIs allows for timely maintenance and adjustments, ensuring that the heat exchanger operates at its optimal capacity, potentially saving industries thousands in operational costs as outlined in the latest reports by the American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE).
| Key Performance Indicator | Description | Optimal Value | Current Value | Action Needed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Efficiency | Ratio of heat transferred to the heat exchange area | > 90% | 85% | Improve flow rates |
| Pressure Drop | Loss of pressure through the heat exchanger | < 5 psi | 6 psi | Evaluate flow paths |
| Flow Rate | Volume of fluid moving through the exchanger | Variable by application | High | Adjust pump speed |
| Maintenance Frequency | Regular inspections and cleanings | 3-6 months | 12 months | Schedule routine maintenance |
| Fluid Temperature | Inlet and outlet temperatures of the fluids | As per design | Lower than expected | Check for fouling |

Regular maintenance is crucial for enhancing the performance of plate heat exchangers (PHEs). One essential tip is to establish a routine inspection schedule. Regularly checking for signs of wear, corrosion, or fouling can help identify potential issues before they escalate. During inspections, it’s important to examine the gaskets and plates for any damage, as these components are vital for optimal operation. Early detection can lead to timely repairs and significant cost savings.
Another effective maintenance practice involves cleaning the heat exchanger thoroughly. Depending on the application, fouling can occur due to sediment, scaling, or biological growth. Implementing a scheduled cleaning protocol using appropriate methods, such as chemical cleaning or high-pressure water jetting, can effectively restore the efficiency of the heat exchanger. Additionally, monitoring the operating conditions, such as temperature and pressure, ensures that the PHE is functioning within its designed parameters, which ultimately prolongs its lifespan and performance.
Finally, training the maintenance staff on the specifics of PHE operation and care enhances overall performance. Knowledgeable personnel can make informed decisions regarding repairs and maintenance, ensuring that the heat exchanger consistently operates at peak efficiency.
When optimizing heat exchangers, particularly plate heat exchangers (PHEs), several design considerations play a crucial role in achieving optimal heat transfer. One of the most significant factors is the selection of the correct heat transfer fluid. Not all fluids are suitable for every application; their thermal properties, viscosity, and compatibility with materials are essential to ensuring efficient heat transfer and system longevity. The choice of fluid can significantly impact the temperature range within which the system operates effectively, aligning with industry standards such as those set by ASHRAE.
Furthermore, geometric configurations of the heat exchanger, such as fin count and diameter ratios, can enhance performance. A well-designed PHE can adapt to varying operational conditions, balancing the trade-off between cost and flexibility in process heat recovery solutions. As technologies evolve, particularly in sectors like AI and cloud computing, the incorporation of innovative heat exchanger designs is paramount. These designs not only need to accommodate the increasing demands for efficiency but also ensure reliability across different operational scenarios.
This chart displays 10 essential tips for optimizing Performance of Plate Heat Exchangers (PHE) based on common design considerations for optimal heat transfer.
When troubleshooting issues related to plate heat exchangers (PHE), it’s crucial to identify the root causes of inefficiencies. Common problems such as fouling, corrosion, and flow maldistribution can significantly impair performance. Regular inspections and maintenance schedules can mitigate these issues before they escalate. For instance, fouling can be addressed by implementing effective cleaning protocols, which can involve chemical cleaning agents or mechanical methods to remove buildup on plates. Routine analysis of the fluid characteristics is vital in preventing such issues.
In addition to fouling, operators should monitor temperature differentials and pressure drops across the PHE. An unexpected increase in pressure drop might indicate blockages or damage, while a reduced temperature differential could suggest insufficient thermal contact between the plates. By regularly recalibrating sensors and tracking performance metrics, operators can identify anomalies early. Developing a systematic approach to maintaining and troubleshooting PHEs not only enhances operational efficiency but also extends the lifespan of the equipment.