Leave Your Message
In the complex world of thermal management, understanding the essential Heat Exchanger Parts is crucial. Experts like Dr. Emma Larson, a leading specialist in heat exchanger technology, emphasize, “Every part plays a vital role in efficiency.” Each component must work in harmony for optimal performance.
Heat exchangers feature various parts such as tubes, fins, and gaskets. Each serves a unique function, contributing to overall system effectiveness. For instance, tubes facilitate heat transfer, while fins increase surface area. Gaskets ensure tight seals, preventing leaks. Yet, improper maintenance can lead to inefficiencies.
Understanding Heat Exchanger Parts can seem overwhelming. However, knowledge of each component leads to better decision-making. Consideration for these parts often brings forth questions about their longevity and efficiency. Analyzing performance and seeking improvement are essential steps towards maximizing energy transfer.

Heat exchangers are vital in various industrial processes. They transfer heat between fluids while preventing direct contact. Understanding their essential components helps in selecting and maintaining them effectively.
The main parts include tubes, shell, and baffles. Tubes carry the fluids, allowing for efficient heat transfer. Shells contain the tubes and help isolate different fluids. Baffles direct the flow, maximizing heat exchange. Inadequate baffle design can lead to poor heat transfer.
Additionally, gaskets and end caps play critical roles. Gaskets prevent leaks and maintain pressure. End caps secure fluid inside the heat exchanger. Regular inspection of these components is crucial; neglect can lead to operational failures or efficiency loss. It's important to be aware of wear and tear that might not be immediately visible.
In heat exchanger systems, tubes play a crucial role. They facilitate the transfer of heat between two fluids. These fluids can be gases or liquids, each moving through different tubing pathways. The material and design of the tubes affect efficiency. Copper and stainless steel are common materials due to their high thermal conductivity.
Heat exchanger tubes come in various shapes. Some are straight, while others are coiled. Coiled tubes often provide better heat transfer. Their shape helps increase surface area, leading to improved performance. Moreover, the diameter of the tubes influences flow rates. Larger tubes can handle more fluid but may reduce heat transfer efficiency.
Tips: Regular maintenance of tubes is essential. Check for corrosion or scaling that could hinder performance. Also, consider using tube cleaning methods to ensure optimal heat exchange. Monitoring fluid temperatures is equally important. It can help identify issues early on, preventing costly repairs down the line.
Headers and manifolds play a crucial role in heat exchangers. They guide fluid flow and ensure even distribution across the heat transfer surfaces. Without well-designed headers, fluid can become unevenly distributed. This can lead to hot spots, causing inefficiencies in heat transfer.
According to a report by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, about 30% of heat exchanger failures relate to poor fluid distribution. When the heat transfer surfaces are not utilized effectively, the overall performance drops. It's clear that the design of headers and manifolds demands careful consideration. Even slight inefficiencies can add up. For instance, multiple studies indicate that optimizing headers can improve efficiency by over 20%.
Moreover, improper maintenance can hinder their performance. It’s easy to overlook these parts, yet they are vital. Regular inspections can help identify potential issues. Industry experts suggest that focusing on headers and manifolds can enhance the reliability of heat exchangers. This is an area worth exploring for anyone involved in thermal management. Even small adjustments here can yield significant gains.
Fins play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of heat exchangers. They increase the surface area available for heat transfer, allowing machines to operate more effectively. According to a recent industry report, using fins can improve heat transfer rates by up to 50%. This significant enhancement highlights their importance in various applications.
The design and placement of fins can vary. Some fins are simple and flat, while others are shaped to promote airflow. The choice of fin design can dramatically affect performance. Studies indicate that optimizing fin configurations can lead to further efficiency improvements. However, not all fin designs yield the best results. Suboptimal designs may result in turbulence and reduced performance. Design flaws often lead to wasted energy and higher operational costs.
Fins also require careful material selection. The right material must balance thermal conductivity and durability. Common materials include aluminum and copper, but their costs can vary widely. Price fluctuations in raw materials complicate decisions for manufacturers. Choices must consider not just immediate costs but long-term efficiency and maintenance. Each choice reflects an ongoing challenge in heat exchanger design.
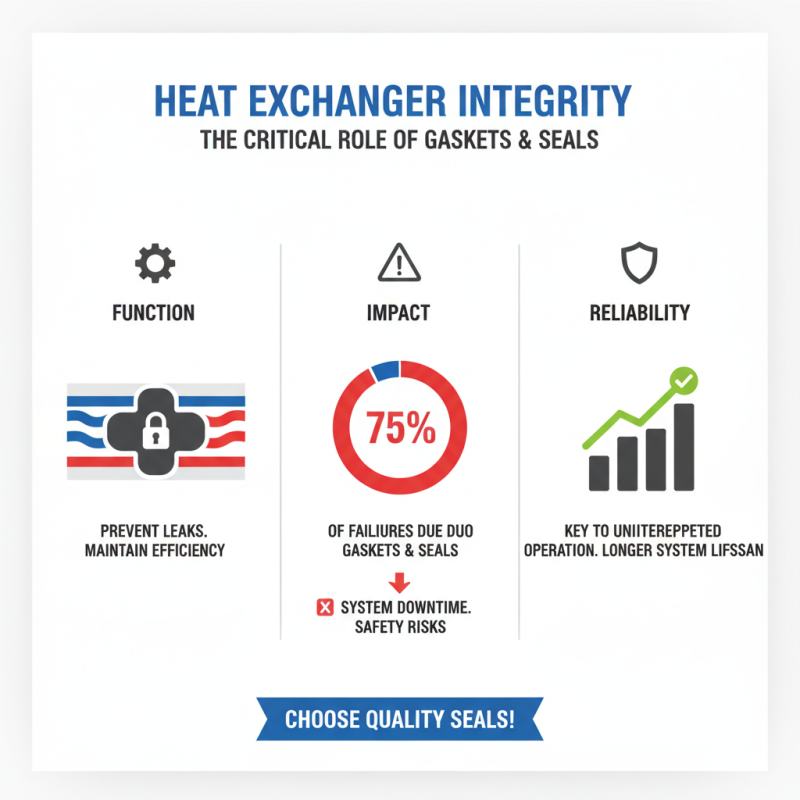
In heat exchangers, gaskets and seals play a crucial role in maintaining integrity. They ensure that fluids do not leak, which can lead to system inefficiencies and potential hazards. According to industry reports, 75% of heat exchanger failures are attributed to gasket and seal failures. This highlights their importance in overall system reliability.
Gaskets act as a barrier between two surfaces. They help manage pressures and temperatures effectively. A study from the Thermal Engineering Journal noted that improper installation of gaskets can result in an 18% increase in energy losses. Such losses are significant, especially in high-demand industrial settings.
Seals, on the other hand, prevent fluid ingress. When seals degrade, the risk of contamination rises. This not only affects performance but can also damage components downstream. Regular maintenance is essential to spot wear and tear early. Experts recommend replacing seals every one to three years in rigorous applications. However, many facilities overlook this, potentially leading to costly repairs. Therefore, understanding the roles of gaskets and seals is vital for ensuring operational efficiency in heat exchangers.