Leave Your Message
In today's industrial landscape, the efficient management of thermal energy is critical for enhancing productivity and sustainability. The choice of the right heat exchanger PHE (plate heat exchanger) can significantly impact the operational efficiency of various industrial processes. According to a recent report by Grand View Research, the global heat exchanger market is projected to reach USD 22.54 billion by 2025, with plate heat exchangers gaining considerable traction due to their compact design and superior thermal efficiency. These devices are particularly favored in sectors such as chemical processing, oil and gas, and food and beverage, where precise temperature control is essential.
Selecting the appropriate heat exchanger PHE involves a thorough understanding of the specific thermal requirements and operating conditions of an industrial application. Factors such as the type of fluids being processed, the desired heat transfer capacity, and the pressure drop limitations play a pivotal role in this decision-making process. Furthermore, the increasing emphasis on energy conservation and regulatory standards has led to advancements in PHE designs, making them more efficient and environmentally friendly. As industries strive to meet these challenges, making an informed choice on heat exchanger PHEs becomes paramount in securing competitive advantages and achieving operational excellence.

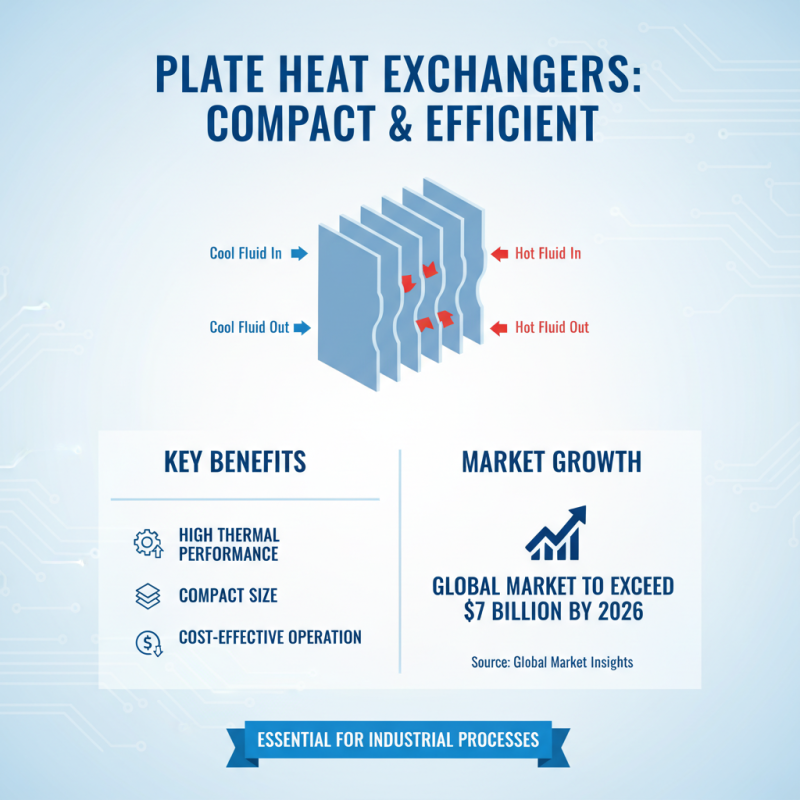
Heat exchangers are essential components in various industrial processes, aiding in the transfer of heat between fluids without mixing them. The design and selection of heat exchangers can significantly impact the efficiency, safety, and operational costs of a plant. In particular, plate heat exchangers (PHEs) are gaining popularity due to their compact size and high thermal performance. According to a recent report by the Global Market Insights, the plate heat exchanger market is expected to surpass $7 billion by 2026, indicating growing demand across industries.
Understanding the fundamental principles of heat transfer and the specific requirements of your application is crucial in selecting the right PHE. Factors such as thermal conductivity, fluid properties, and temperature ranges play vital roles in determining the most efficient heat exchanger design. For instance, a study from the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) highlighted that well-designed PHEs can achieve up to 90% heat transfer efficiency. This suggests that proper evaluation of parameters—including flow rates, pressure drops, and fouling tendencies—will lead to enhanced performance and reduced operational costs.
In addition, maintenance and cleaning protocols must be considered when selecting a heat exchanger type. A report from the European Heat Exchanger Manufacturers Association indicates that regular maintenance can extend the life cycle of a PHE by up to 30%, minimizing downtime and capital expenditures. By understanding these basics, industrial facilities can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and economic objectives, ensuring optimal heat exchanger performance and industry sustainability.
Identifying your industrial heat transfer requirements is crucial for selecting the appropriate heat exchanger. Begin by understanding the specific processes within your facility that necessitate heat exchange. Factors such as the type of fluids involved, temperature ranges, flow rates, and pressure conditions all play a significant role in determining the right heat exchanger design. For instance, applications involving aggressive fluids or high temperatures may require specialized materials and configurations to ensure efficiency and durability.
Next, consider the operational environment of your heat exchanger. Different industries may place unique constraints on space, maintenance access, and operational safety. For heavy industrial settings, modular and compact designs might be advantageous for space efficiency, while industries focused on hygiene, like food processing, will have stricter cleanliness standards. Conducting a thorough assessment of these factors will help you identify the heat transfer requirements essential for your industrial processes, ensuring that you select a heat exchanger that maximizes efficiency and meets compliance standards.
| Heat Exchanger Type | Material | Operating Temperature (°C) | Pressure Drop (bar) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shell and Tube | Stainless Steel | 150 | 2.5 | Oil Refining, Chemical Processing |
| Plate | Titanium | 120 | 1.0 | Food Industry, Pharmaceutical |
| Air-Cooled | Aluminum | 50 | 0.5 | Power Generation, HVAC |
| Double Tube | Copper | 100 | 1.5 | Marine Applications, Refrigeration |
| Finned Tube | Carbon Steel | 200 | 3.0 | Gas Processing, Chemical Plants |
When selecting the right heat exchanger plate heat exchanger (PHE) for your industrial needs, it’s crucial to evaluate various designs and materials based on their performance characteristics and suitability for your application. There are multiple types of PHEs, including gasketed, welded, and semi-welded designs. Gasketed PHEs offer flexibility for maintenance and cleaning, making them ideal for applications where regular servicing is required. On the other hand, welded PHEs are often used in high-pressure applications due to their robust construction, although they lack the ease of access for cleaning.
Materials also play a significant role in the performance and longevity of PHEs. Common materials include stainless steel, titanium, and various alloys. Stainless steel is widely preferred due to its excellent corrosion resistance and durability, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. Titanium, while more expensive, is advantageous in corrosive environments, ensuring a longer lifespan despite the initial investment. In contrast, the choice of material should be closely aligned with the fluids being processed and the operating conditions.
Tips: Always consider the specific operating conditions, including temperature and pressure, when selecting PHE materials. Consult with industry professionals to ensure that the chosen design aligns with your efficiency goals. Regular maintenance checks can extend the life of your heat exchangers and improve system performance.
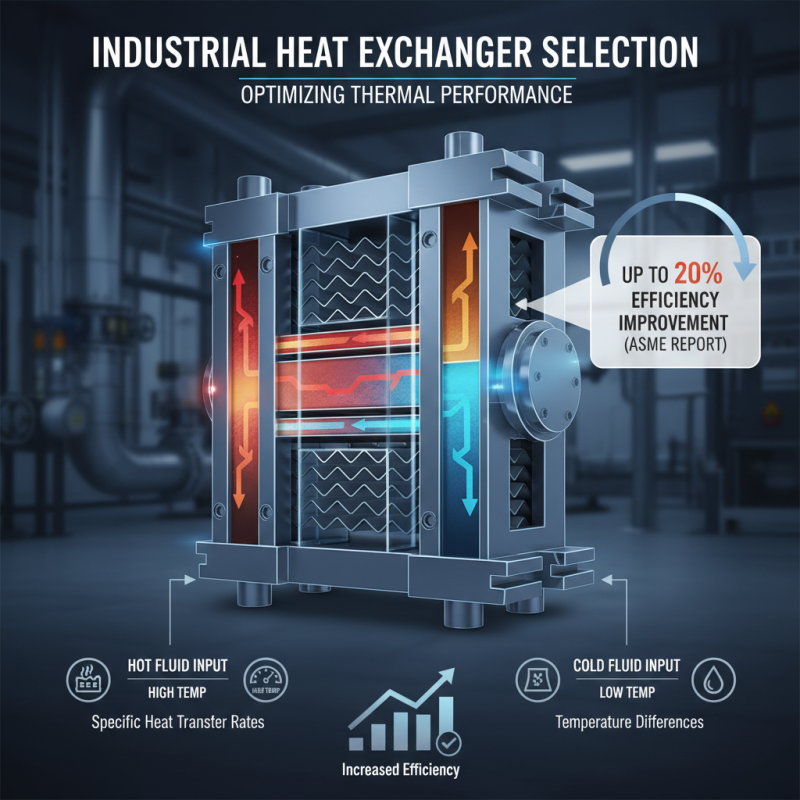
When selecting the right heat exchanger PHE (plate heat exchanger) for industrial applications, several factors play a crucial role in ensuring efficiency and optimal performance. One of the primary considerations is the thermal performance required by the application. For instance, a report from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) indicates that a well-designed heat exchanger can enhance thermal efficiency by up to 20%. Therefore, understanding the specific heat transfer rates and temperature differences in your system will help narrow down the options.
Another important factor is the fluid characteristics, including viscosity, thermal conductivity, and potential for fouling. According to industry estimates, high-viscosity fluids can reduce heat transfer efficiency by as much as 30% if not properly accounted for in the selection process. It's essential to assess whether the fluids involved can impact the PHE’s overall performance. Different designs may be needed to handle aggressive or non-Newtonian fluids effectively.
Tips: When evaluating your options, consider using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software to simulate various scenarios. This can provide valuable insights into flow patterns and potential hotspots, ensuring a more informed decision. Additionally, always check for maintenance compatibility, as the ease of cleaning and servicing can significantly impact long-term efficiency and operational costs.
When selecting a heat exchanger PHE (plate heat exchanger) for industrial applications, it is crucial to consider the operating conditions to ensure optimal performance. The temperature and pressure of the fluids involved can significantly influence the efficiency and durability of the heat exchanger. If the operating conditions vary widely, it is essential to choose materials resistant to corrosion and thermal stress. Additionally, the flow rates of the fluids should align with the specifications of the PHE to maintain proper heat transfer without causing damage or excessive wear.
Regular maintenance plays a vital role in sustaining the performance of a heat exchanger. This includes routine inspections to detect any signs of fouling or scaling, which can impede heat transfer efficiency. Cleaning schedules should be established based on the specific fluid properties and operating conditions, as well as the manufacturer’s recommendations. Furthermore, monitoring temperature differentials and pressure drops can provide early indications of performance decline, allowing for timely interventions. Adhering to maintenance protocols not only extends the lifespan of the heat exchanger but also ensures optimal energy efficiency within the industrial system.