Leave Your Message
Choosing the right Plate To Plate Heat Exchanger is crucial for efficient thermal management. This type of heat exchanger is widely used in many industries. It offers various advantages, like compact design and high efficiency. However, not all exchangers are suitable for every application.
When selecting a Plate To Plate Heat Exchanger, consider factors such as material compatibility, pressure drops, and temperature ranges. It’s easy to overlook these specifics. Many users focus on brand or price alone. They might regret their choice later when performance issues arise.
You must also think about maintenance needs. Some designs require more upkeep than others. Inadequate attention to maintenance can lead to failures. Identify your unique needs to make a better decision. Ultimately, a thoughtful selection ensures reliable operation and energy efficiency.
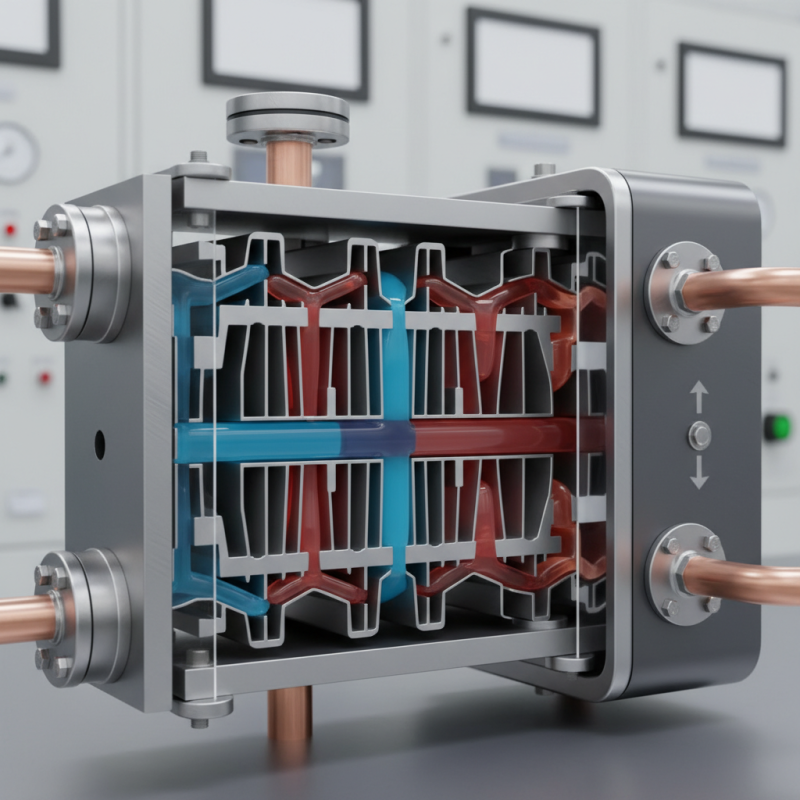
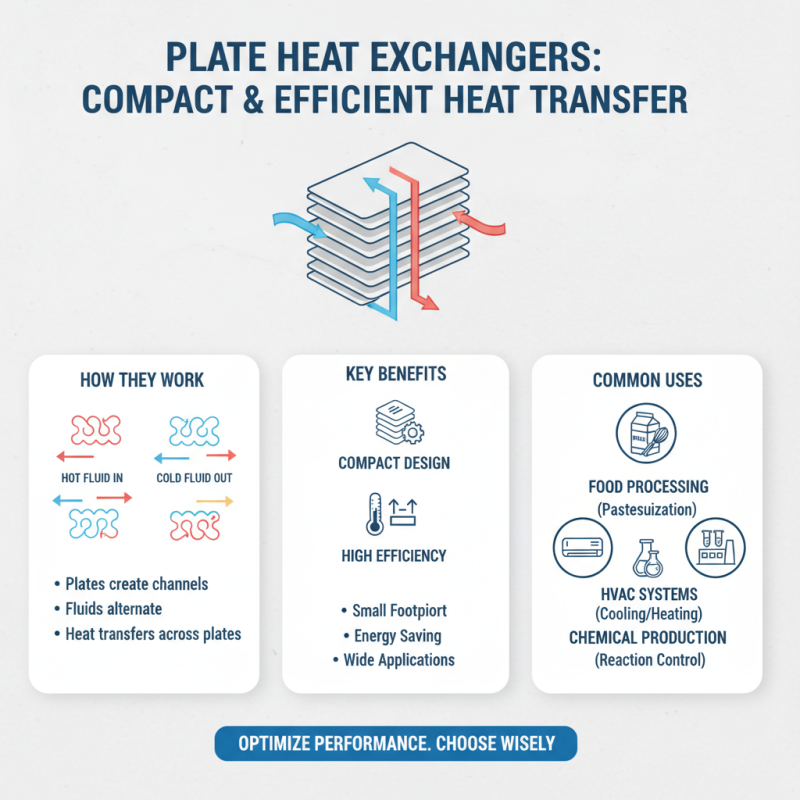
Plate to plate heat exchangers are essential in many industries. They efficiently transfer heat between two fluids. Their compact design allows for high performance in small spaces. Common applications include food processing, HVAC systems, and chemical production. Understanding the various types and configurations is crucial to make the right choice.
When selecting a plate to plate heat exchanger, consider your flow rates and temperatures. Each application has unique requirements. For example, food processing requires careful cleaning protocols, while chemical industries need robust materials. It's also important to think about maintenance. Some designs are easier to clean than others. Regular maintenance ensures efficiency and longevity but can be neglected.
**Tip:** Always assess the thermal efficiency during your selection process. A higher efficiency may save costs in the long run.
Think about your space constraints. Larger heat exchangers might not fit, despite their efficiency. In some cases, a smaller unit can provide adequate performance. This choice can seem counterintuitive but is worth exploring.
**Tip:** Consult with experts when in doubt. Their insights can clarify your options and lead to better decisions.
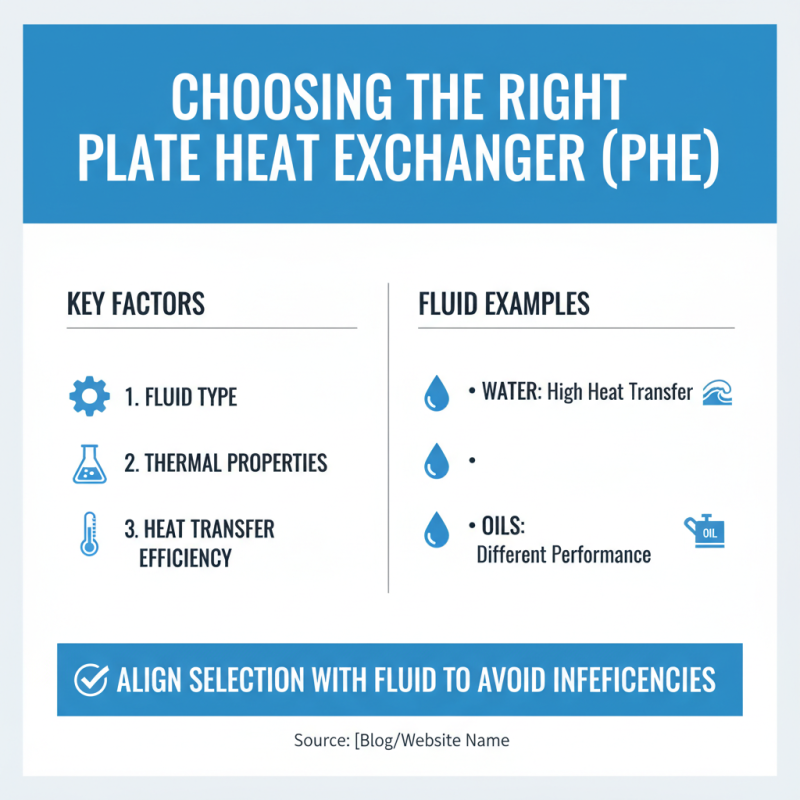
Choosing the right plate heat exchanger (PHE) involves understanding key factors that directly impact performance. One critical factor is the type of fluid you will be processing. Different fluids have varying thermal properties, which can affect heat transfer efficiency. For example, water typically has a high heat transfer coefficient, while oils may perform differently. Ensure your choice aligns with the specific fluid to avoid inefficiencies.
Material selection is equally important. Most plate heat exchangers are made of stainless steel or titanium. Stainless steel works well for water and brine, while titanium is best for seawater applications. This choice directly influences durability and resistance to corrosion. A report by the Heat Exchanger Institute indicates that up to 30% of maintenance costs arise from material-related issues. This highlights the need for careful selection.
**Tip:** Keep maintenance in mind. Regular inspections can prevent costly downtime.
Another consideration is the flow arrangement. Counterflow configurations offer better efficiency for heat transfer. Meanwhile, parallel flow setups are simpler but less effective. Evaluating your operational requirements is essential. Note that many businesses overlook this, leading to lower output than potential.
**Tip:** Consult with engineering professionals. They can provide insights tailored to your specific needs.
Choosing the right material for your plate to plate heat exchanger can significantly impact performance. Stainless steel is popular. It offers excellent corrosion resistance. This makes it ideal for many industries. However, it can be costly. For some applications, this may not be justified.
On the other hand, titanium is another option. It excels in aggressive environments. Yet, its price may deter many users. Not all operations require exotic materials. Carbon steel or even plastic can work in less demanding settings. Consider the fluid types and temperatures involved.
Remember, durability matters. A cheaper material may save money upfront, but could lead to failures. Evaluate the long-term operational costs. Frequent replacements can negate initial savings. Reflect on how often you’ll need maintenance. Each material has limits. Know your needs before making a choice.
| Material Type | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Corrosion Resistance | Operating Temperature (°C) | Durability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | 15-25 | High | -40 to 400 | Excellent |
| Titanium | 17-30 | Very High | -60 to 300 | Very Good |
| Copper | 390 | Low | -40 to 200 | Good |
| Nickel Alloy | 8-12 | High | -250 to 800 | Excellent |
| Aluminum | 205 | Medium | -50 to 350 | Good |
When selecting a plate-to-plate heat exchanger, understanding flow patterns and heat transfer requirements is crucial. Flow patterns, such as parallel, counterflow, and crossflow, significantly affect thermal efficiency. Reports indicate that counterflow configurations can enhance heat transfer by up to 30%. This is due to their ability to maintain a higher temperature gradient throughout the heat exchanger.
Heat transfer requirements depend on multiple factors. Fluid properties, such as viscosity and specific heat, influence performance. A study revealed that fluids with higher viscosity may lead to lower heat transfer efficiency. This prompts the need for careful analysis and sometimes adjustment in design. It is essential not to overlook the potential for scaling and fouling, which can impair performance. Smaller plates may amplify these issues, leading to increased maintenance.
Selecting the right materials also plays a role. Corrosive environments can deteriorate certain materials faster. Understanding the fluid composition is necessary. This ensures the chosen material can withstand the operational conditions. Ultimately, achieving the right balance of flow patterns and material selection requires thoughtful consideration and, at times, experimentation. It can be a challenging endeavor, but attention to detail is vital for optimizing performance.
When it comes to plate to plate heat exchangers, maintenance is key. Regular checks can prevent significant issues. Inspections should focus on leaks and blockages. Observing temperature and pressure changes helps identify problems early.
Tips: Clean the plates regularly to avoid scaling. Ensure proper coolant flow to maintain efficiency. This will prolong the equipment’s life.
Operational considerations also impact longevity. Monitor the working environment. High temperatures can increase wear and tear. Ensure that seals and gaskets are intact. Replacing worn parts can save you from expensive repairs.
Tips: Train staff regularly on best practices. Use performance data to forecast maintenance needs. These proactive steps help avoid unexpected downtimes.
This chart compares the efficiency of different plate to plate heat exchangers based on their maintenance and operational considerations. The data reflects average thermal conductivity and heat transfer rates for various models.






